Magento Explained: Understanding The Magento Ecosystem

In this article, we’re going to explain some of the terminology new eCommerce merchants need to understand before embarking on their journey with Magento.
First things first, what is Magento?
Magento is a powerful eCommerce application built on open source technology. It’s used by retailers ranging from solo entrepreneurs to big-name eCommerce merchants like Ford, Wrangler, Silent Night, Harvey Nichols, Paul Smith, and Christian Louboutin.
Magento was initially released in March 2008 and has since grown to incredible proportions. There have been two main iterations of the application (Magento 1 and Magento 2).
One of the main reasons why eCommerce developers love Magento is due to its customizability and ability to scale as a business grows. A huge number of plugins and extensions are available for store developers, and custom functionality can be included with help from a Magento developer.
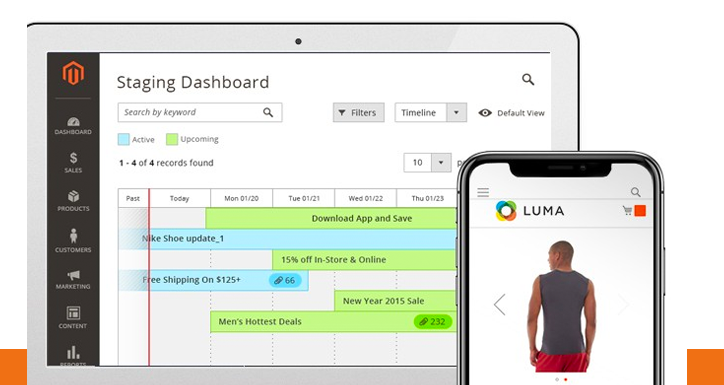
Image credit: Magento Commerce
The heart of the Magento ecosystem is an open source community of developers. The community is maintained by the Magento company. Magento Commerce is that company’s commercial offering, and includes support and additional features for enterprise retailers. This includes dedicated Magento account management.
Originally released in 2016, the self-hosted version of Magento Commerce was previously known as Magento Enterprise Edition. It has since grown to become a staple in the Magento community with bigger eCommerce businesses looking for more functionality looking for greater complexity and with a larger global presence.
If you’re a larger eCommerce business, Magento Commerce is likely the best option for your business.
Magento Open Source is a free version of Magento that includes many of the same features as Magento Commerce. Until recently, Magento Open Source was known as Magento Community Edition.
Magento commerce was originally released in 2007 as a public beta. The full version was released in 2008. Because Magento Open Source is open source, developers are not locked into the software they are provided. It is possible to make changes to the application and incorporates other technologies as well. This means that developers can craft Magento Open Source into something specific to their needs. Something developers aren’t as free with when it comes to Magento Commerce.
There is an impressive base feature set with Magento Open Source, yet where it really shines is in the additional features offered through the countless extensions currently in circulation. At the time of writing, there are more than 10,000 extensions available in the Magento marketplace.
To use Magento Open Source, retailers can choose a Magento hosting provider, which will provide the servers, bandwidth, and support a retailer needs to build their store. This also allows for Magento store owners to focus on what’s important – their store – and leave background processes to someone else.
There are other differences between the Open Source and Commerce editions of Magento. Here a few more in more detail.
| Features | Opensource | Commerce |
| Responsive eCommerce website | ✔ | ✔ |
| Promotions Engine / Product & Catalog Management | ✔ | ✔ |
| Checkout, Payment, Shipping & Order Management | ✔ | ✔ |
| Site management (admin) | ✔ | ✔ |
| ElasticSearch | ✕ | ✔ |
| Bluefoot CMS in 2.2 | ✕ | ✔ |
| Magento Order Management | ✕ | ✔ |
| Content Staging & Preview | ✕ | ✔ |
| Magento Shipping | ✕ | ✔ |
| OOTB B2B Functionality (in v2.2) | ✕ | ✔ |
Magento is a complete eCommerce solution, but retailers can add extra functionality by installing extensions created by third-party developers. Magento extensions extend or enhance Magento’s existing features. Hostdedi has created several Magento extensions, including the popular Turpentine extension for Varnish integration, and Alarmbell, a Magento security extension.
There are hundreds of Magento extensions, both free and premium. Magento users should take care to only install extensions from reputable developers or marketplaces. If in doubt, head to the official Magento Marketplace, which we’ll discuss in a moment.
Magento themes are similar to extensions, except themes focus on the design of a site rather than on adding new functionality. Every Magento store uses a theme, and just like extensions, there are free themes, paid premium themes, and custom themes developed for specific retailers.
Magento Marketplace is an officially supported repository of both extensions and themes. Magento Marketplace thoroughly vets all extensions and themes it distributes, so you can be sure that everything you find on there is secure and useful.
Magento Marketplace isn’t the only trustworthy source of themes and extensions. Many reputable developers have their own sites and stores. However, if you’re unsure of the quality of a theme or extension, it’s good practice to check to see if it’s on the marketplace.
Finally, Magento hosting: every eCommerce store needs a hosting provider. The hosting provider takes care of the store’s connection to the internet, the server the Magento application and its database run on, and the support retailers need to provide a fast shopping experience to their users.
Hosting providers are of varying quality and Magento requires specific conditions to provide the best performance and reliability. Choosing a specialist Magento optimized hosting provider with great support is the best way to start your journey as an eCommerce retailer
Posted in:
Magento